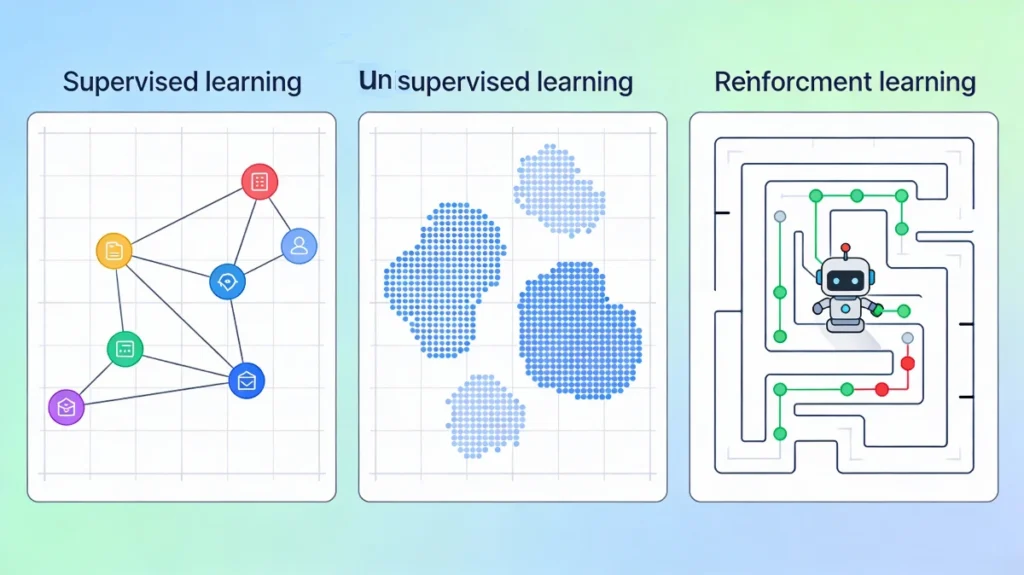
Machine Learning is not a single technique. Instead, it is divided into different learning approaches based on how data is provided to the model.
The three most important types are:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
In this article, we’ll explain each type in simple language, with real-world examples, so you can clearly understand how they differ.
Why Are There Different Types of Machine Learning?
Different problems require different learning methods.
- Sometimes we already know the correct answers
- Sometimes we only have raw data with no labels
- Sometimes a system must learn by trial and error
That’s why Machine Learning is divided into these three categories.
1. Supervised Learning
Supervised Learning is the most commonly used type of Machine Learning.
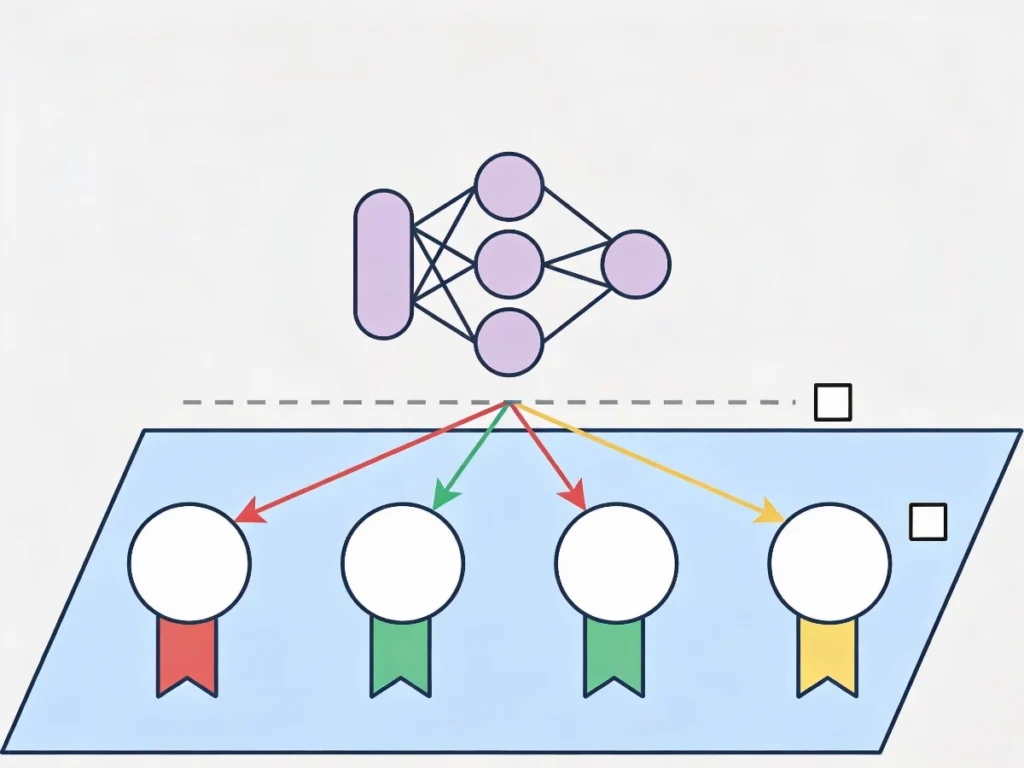
How it works
- The model is trained using labeled data
- Each input already has a correct output
- The model learns by comparing predictions with known answers
Think of it like a student learning with an answer key.
Simple example
Email spam detection:
- Emails are labeled as “Spam” or “Not Spam”
- The model learns patterns from these labels
- New emails are classified automatically
Common uses
- Email spam filtering
- House price prediction
- Credit score analysis
- Medical diagnosis systems
2. Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning works without labeled data.
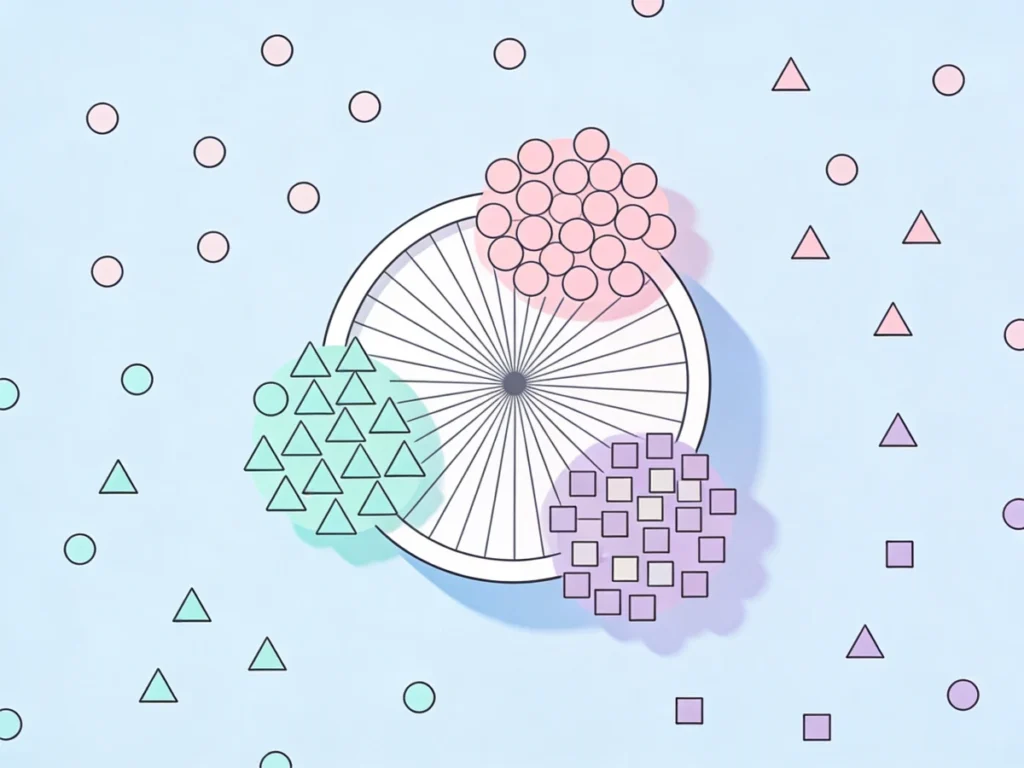
How it works
- The model receives raw data
- No correct answers are provided
- The model discovers patterns on its own
This is like exploring information without guidance.
Simple example
Customer segmentation:
- An online store has customer data
- No predefined groups exist
- The model groups customers based on behavior
Common uses
- Market segmentation
- Recommendation systems
- Pattern discovery
- Anomaly detection
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning teaches models through experience and rewards.
How it works
- The model takes actions
- It receives feedback as rewards or penalties
- Over time, it learns the best strategy
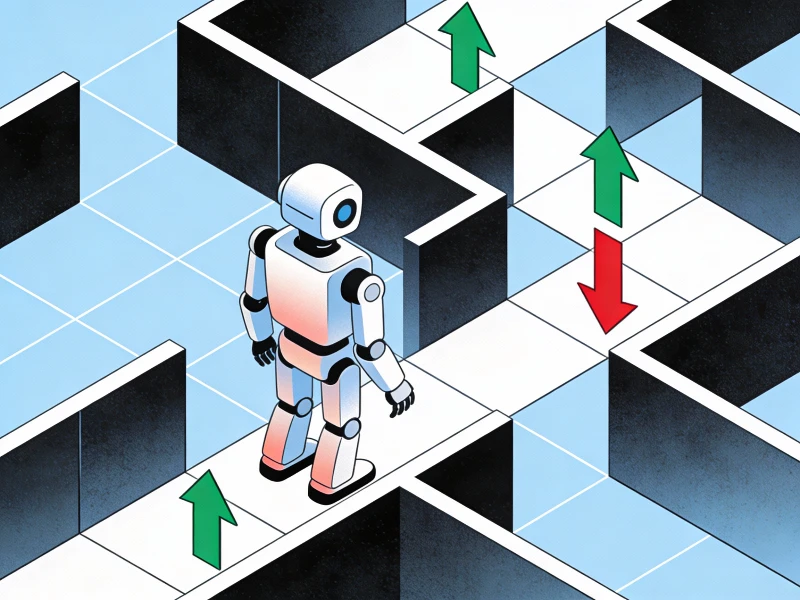
This is similar to how humans learn through practice.
Simple example
Game-playing AI:
- The AI makes a move
- If it wins, it gets a reward
- If it loses, it receives a penalty
- Over time, performance improves
Common uses
- Robotics
- Self-driving cars
- Game AI
- Smart decision systems
Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Supervised | Unsupervised | Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data labels | Yes | No | No |
| Learning style | Guided | Self-discovery | Trial & error |
| Human feedback | Required | Not required | Reward-based |
| Common use | Prediction | Pattern finding | Decision making |
Which Type Is The Best?
There is no single best type of Machine Learning.
- Use Supervised Learning when labeled data is available
- Use Unsupervised Learning when discovering patterns
- Use Reinforcement Learning when actions and rewards matter
Each serves a different purpose.
How These Types Work Together in Real Life
Modern AI systems often combine multiple learning approaches.
Example:
- Supervised Learning for initial training
- Unsupervised Learning for pattern discovery
- Reinforcement Learning for optimization
This combination makes systems smarter and more adaptable.
How This Fits Into Artificial Intelligence
All three learning types are part of Artificial Intelligence, allowing machines to:
- Learn from data
- Adapt to new situations
- Improve over time without explicit programming
Final Thoughts
Understanding the difference between supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning helps you grasp how modern AI systems work behind the scenes. Each method solves different problems, and together they form the foundation of Machine Learning.