Introduction
Neural networks are the technology behind many modern artificial intelligence systems. From voice assistants and image recognition to self-driving cars and language translation, neural networks help computers understand complex information and make intelligent decisions.
But what exactly are neural networks, and how do they learn from data?
In this article, we will explain neural networks in simple language, step by step, so anyone can understand how artificial brains work without needing technical knowledge.
What Is a Neural Network?
A neural network is a type of machine learning model inspired by the human brain.
Just like the human brain has neurons that send signals to each other, a neural network consists of artificial neurons connected in layers. These neurons work together to process information and learn patterns from data.
Neural networks are used in:
- Image recognition
- Speech recognition
- Language translation
- Medical diagnosis
- Recommendation systems
They are one of the most important building blocks of modern artificial intelligence.
How the Human Brain Inspired Neural Networks
The human brain contains billions of neurons connected by synapses. These neurons:
- Receive signals
- Process information
- Send results to other neurons
Neural networks imitate this process in a simplified way.
In artificial neural networks:
- Neurons are replaced by mathematical units
- Signals are represented by numbers
- Connections are represented by weights
This design allows computers to learn from experience, similar to how humans learn.
Main Parts of a Neural Network
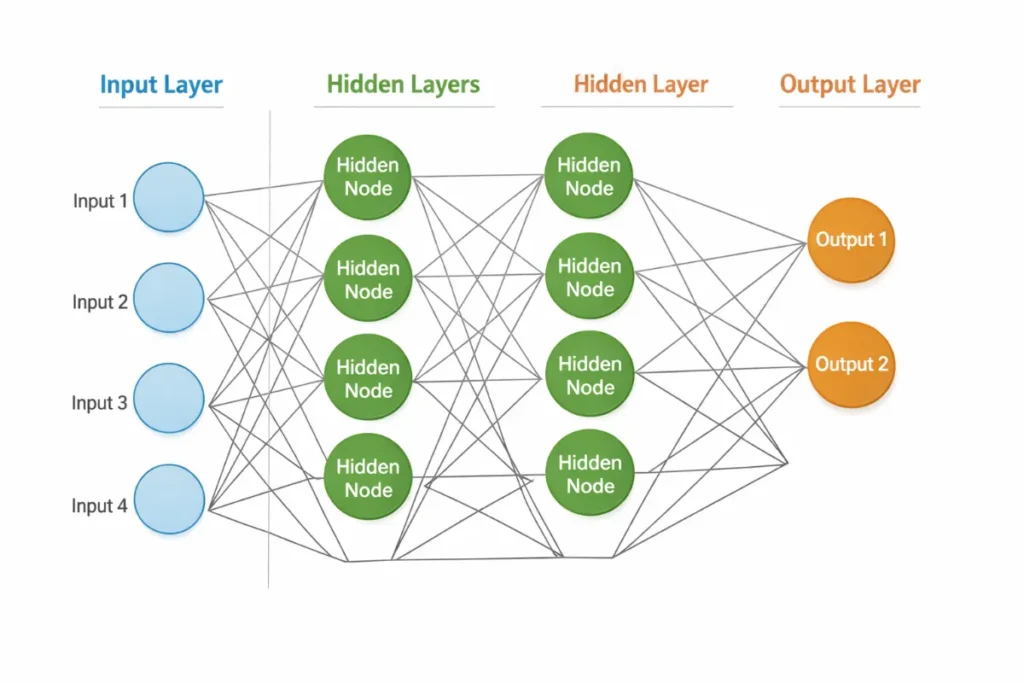
A neural network has three main components:
1. Input Layer
This layer receives the data.
Examples:
- Pixel values from an image
- Numbers from a spreadsheet
- Sound signals from audio
Each input neuron represents one piece of information.
2. Hidden Layers
These are the middle layers where learning happens.
In hidden layers:
- Neurons combine input values
- Apply mathematical operations
- Detect patterns and features
The more complex the task, the more hidden layers the network may have.
3. Output Layer
This layer produces the final result.
Examples:
- Identifying an object in an image
- Predicting a number
- Classifying text as spam or not spam
The output layer gives the network’s decision or prediction.
How Neural Networks Process Information
Each connection between neurons has a weight. These weights determine how important each input is.
The process works like this:
- Inputs enter the network
- Each input is multiplied by a weight
- Values are added together
- An activation function is applied
- The result is passed to the next layer
This process continues until the final output is produced.
How Neural Networks Learn from Data
Learning happens during the training process.
Here is how it works step by step:
Step 1: Provide Training Data
The network receives many examples with correct answers.
Example:
- Images of cats labeled as “cat”
- Emails labeled as “spam” or “not spam”
Step 2: Make Predictions
The network makes an initial guess based on random weights.
At first, predictions are usually wrong.
Step 3: Calculate Error
The system compares its prediction with the correct answer and calculates the error.
This error shows:
- How far the prediction is from the correct result
Step 4: Adjust Weights (Backpropagation)
Using a method called backpropagation, the network:
- Sends the error backward
- Adjusts weights slightly
- Reduces future mistakes
This process repeats thousands of times until the network becomes accurate.
Activation Functions: Helping Networks Make Decisions
Activation functions decide whether a neuron should be activated or not.
They help the network:
- Handle complex patterns
- Add non-linearity
- Improve learning ability
Common activation functions:
- ReLU
- Sigmoid
- Tanh
These functions play a key role in making neural networks powerful and flexible.
Types of Neural Networks
Different types of neural networks are used for different tasks.
1. Feedforward Neural Networks
Information moves in one direction, from input to output.
Used for:
- Basic predictions
- Classification tasks
2. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Specialized for image and video processing.
Used in:
- Face recognition
- Medical image analysis
- Object detection
3. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
Designed for sequential data.
Used in:
- Speech recognition
- Language translation
- Time series prediction
4. Deep Neural Networks
Networks with many hidden layers.
Used in:
- Advanced AI systems
- Deep learning applications
Real-Life Example: How Image Recognition Works

Let us see how a neural network recognizes an image.
- The system receives an image as numbers
- Hidden layers detect edges, shapes, and patterns
- Higher layers recognize objects
- The output layer identifies the object
Over time, the system learns:
- What features define a cat
- What defines a dog
- How to separate different objects
This allows accurate image classification.
Why Neural Networks Are Important
Neural networks make it possible to:
- Recognize speech and images
- Translate languages
- Drive autonomous vehicles
- Diagnose diseases
- Personalize recommendations
They allow computers to solve problems that traditional programming cannot handle easily.
Future of Neural Networks
In the future, neural networks will become:
- More efficient
- More accurate
- Less energy-consuming
- More interpretable
They will play a key role in:
- Healthcare
- Robotics
- Education
- Scientific research
- Smart cities
Neural networks will continue to shape the future of artificial intelligence.
Conclusion
Neural networks are artificial systems inspired by the human brain that learn from data through layered connections and continuous adjustment. By processing information step by step and improving through experience, they enable modern AI applications to understand complex patterns and make intelligent decisions.
Understanding neural networks helps us better appreciate how artificial intelligence is transforming the world around us.

