Deep learning is one of the most important technologies behind modern artificial intelligence. It powers voice assistants, image recognition, self-driving cars, and even recommendation systems used by popular apps and websites. While the term may sound complex, the basic idea behind deep learning is surprisingly simple.
In this article, we will explain what deep learning is, how it works, and where it is used in everyday life, using clear and easy language that anyone can understand.
What Is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn from large amounts of data. These layers allow computers to recognize patterns, make decisions, and improve their performance over time.
In simple words, deep learning helps computers learn in a way that is similar to how the human brain works—by processing information step by step and improving through experience.
How Deep Learning Is Different from Machine Learning
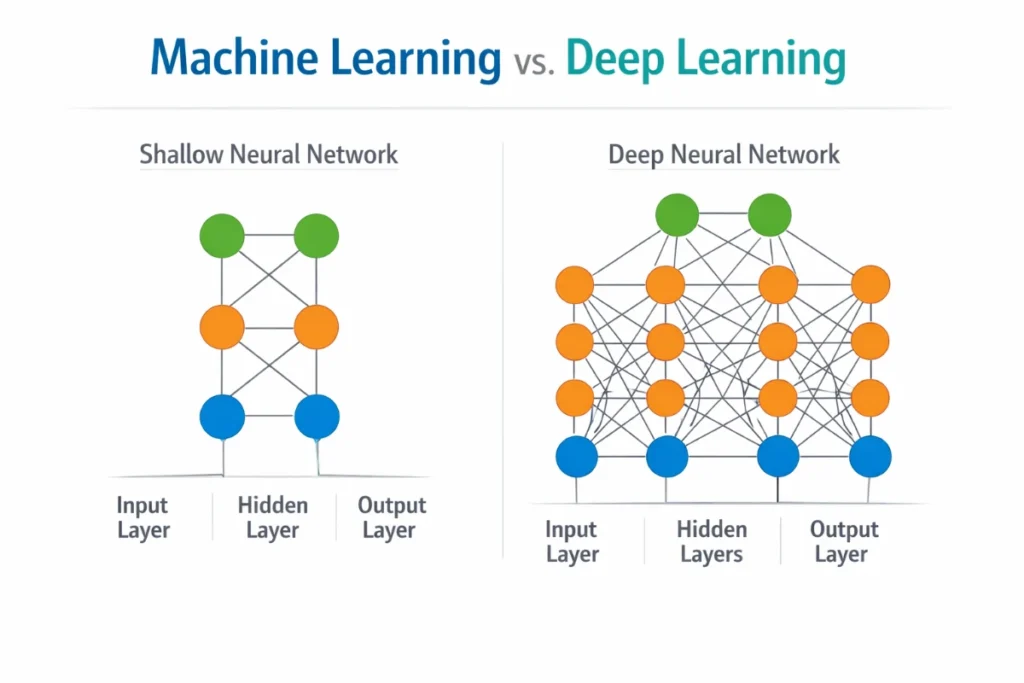
Machine learning usually requires humans to define important features in the data. Deep learning, on the other hand, can automatically learn these features by itself.
For example:
- In traditional machine learning, a programmer might tell the system what to look for.
- In deep learning, the system figures out what is important on its own by analyzing data repeatedly.
This ability makes deep learning especially powerful for handling complex tasks such as images, audio, and language.
How Deep Learning Works (Simple Explanation)
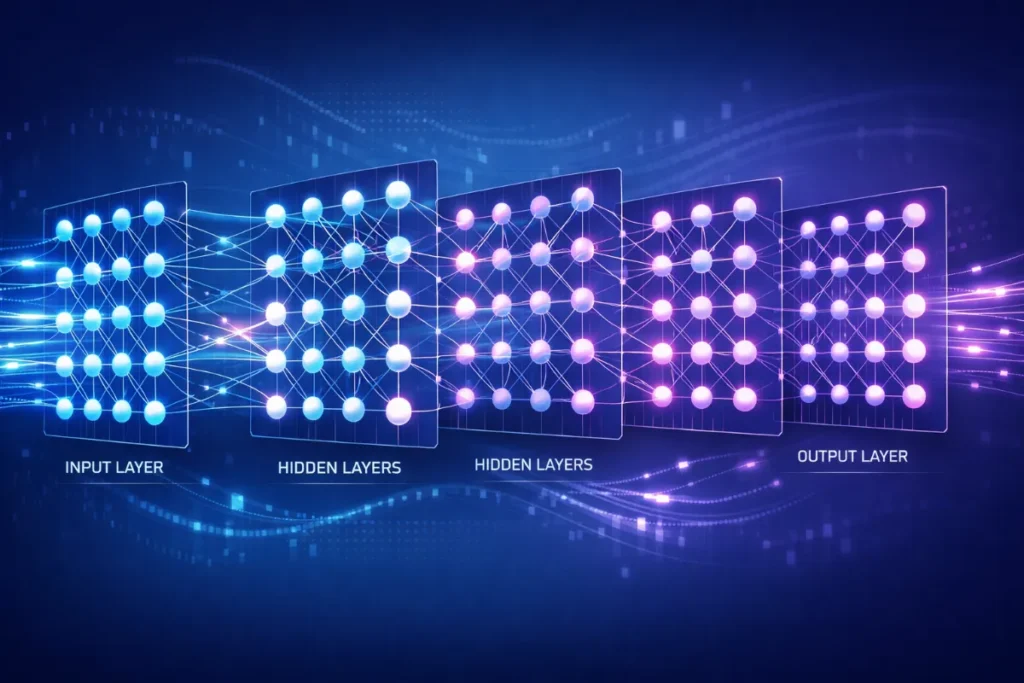
Deep learning uses neural networks, which are made up of layers of connected units called neurons.
These layers include:
- Input Layer – Receives raw data such as images, text, or sound
- Hidden Layers – Process the data and learn patterns
- Output Layer – Produces the final result or prediction
Each time the system processes data, it adjusts internal values to reduce mistakes. Over time, this repeated learning helps the model become more accurate.
Why Is It Called “Deep” Learning?
The word deep refers to the number of layers in the neural network. Traditional neural networks may have one or two layers, while deep learning networks can have many layers, sometimes dozens or even hundreds.
More layers allow the system to learn:
- Simple patterns at first
- More complex patterns at deeper levels
This layered learning approach is what gives deep learning its name.
Real-World Examples of Deep Learning
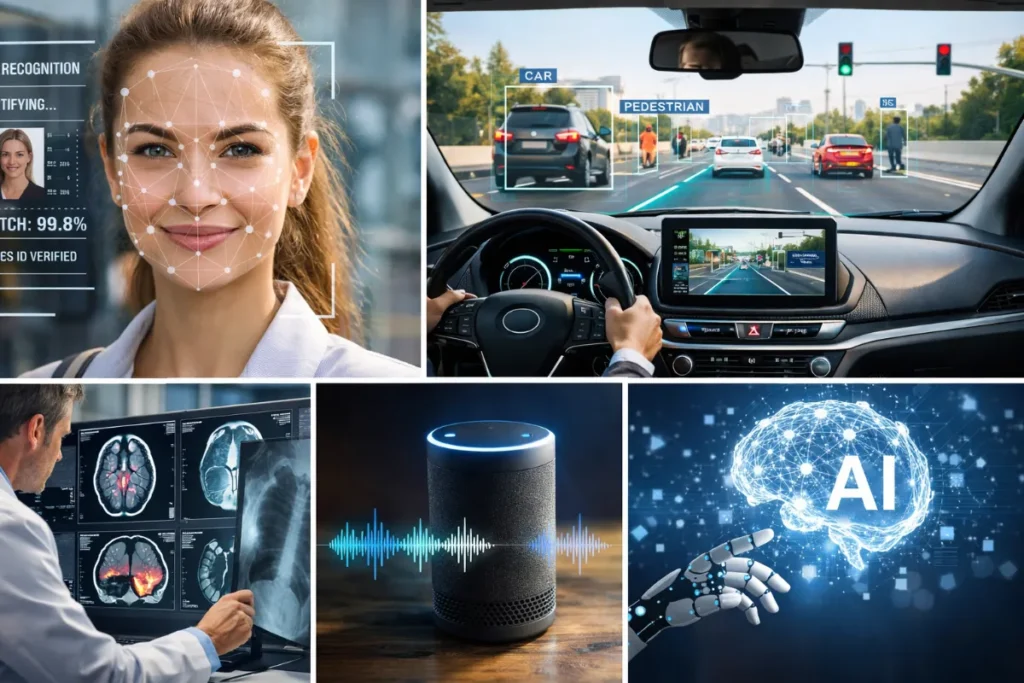

Deep learning is already part of our daily lives, often without us noticing it.
1. Image Recognition
Deep learning helps computers identify faces, objects, and scenes in photos. It is used in phone cameras, security systems, and social media apps.
2. Voice Assistants
Voice assistants use deep learning to understand spoken language and respond accurately. They can recognize accents, tone, and even intent.
3. Self-Driving Cars
Autonomous vehicles rely on deep learning to recognize traffic signs, pedestrians, and road conditions in real time.
4. Recommendation Systems
Streaming platforms and online stores use deep learning to suggest movies, music, and products based on user behavior.
Benefits of Deep Learning
Deep learning offers several advantages:
- Can handle large and complex datasets
- Learns automatically with minimal human input
- Improves accuracy over time
- Works well with images, speech, and text
These benefits make deep learning one of the most powerful tools in modern artificial intelligence.
Limitations and Challenges of Deep Learning
Despite its strengths, deep learning also has limitations:
- Requires a large amount of data
- Needs powerful hardware
- Can be difficult to interpret
- Training can take a long time
Understanding these challenges is important for using deep learning responsibly and effectively.
The Future of Deep Learning
Deep learning will continue to shape the future of technology. It is expected to play a major role in healthcare, education, robotics, and scientific research. As computing power improves and data becomes more available, deep learning systems will become even more capable and efficient.
Conclusion
Deep learning is a key technology behind many intelligent systems we use today. By learning from data through layered neural networks, deep learning allows machines to recognize patterns, make decisions, and improve continuously.
Even though the concept may seem complex, the basic idea is simple: machines learn better by learning deeply from experience. Understanding deep learning helps us better understand the future of artificial intelligence and how it will impact our lives.